Publication
Pakistan's Parallel Foreign Exchange Market
Hundi/Hawala How it works?
© Friedrich Naumann Foundation for Freedom - Pakistan
Hundi/Hawala How it works?
© Friedrich Naumann Foundation for Freedom - PakistanThis is an excerpt from our publication, which you can download in our shop.
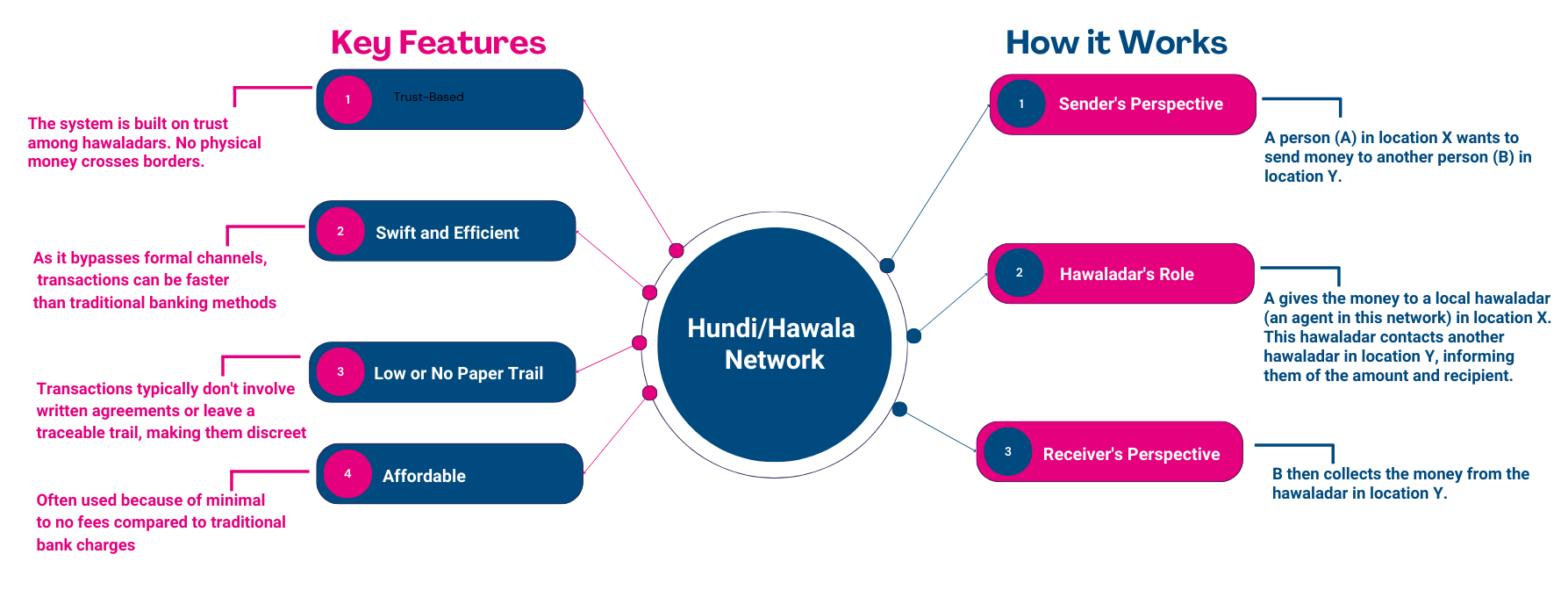
The parallel foreign exchange (FX) market in Pakistan operates alongside the formal banking system, creating a complex and primarily informal financial network. Central to this system is the hundi/hawala network, extensively employed by overseas Pakistanis to remit funds back to their homeland. However, the lack of transparency within this network introduces a heightened risk of fraudulent activities in foreign exchange transactions.
The FX market structure consists of three primary layers: the interbank market, the kerb market, and the hawala brokers:
- The interbank market facilitates approved FX transactions within the formal banking system, determining the official exchange rate through the interplay of demand and supply.
- Conversely, the kerb market, primarily composed of exchange companies, deals with remittances and dollar purchases, offering a more accessible alternative for the public.
- The hawala brokers, operating on trust and social networks, span regions globally, enabling transactions without formal documentation.
The hundi/hawala network and informal sectors present unique regulatory challenges due to their complex and unregulated nature. Balancing the need for regulation to prevent illicit activities with facilitation of legitimate transactions poses a significant policy challenge.
This Policy Paper is authored by Dr Aneel Salman - KSBL-IPRI Chair of Economic Security and Basit Ali - Associate Economic Security at the Islamabad Policy Research Institute (IPRI) in Pakistan.